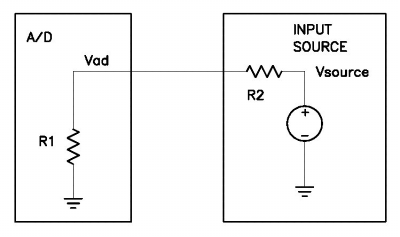
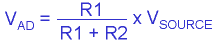
One of the most common sources of error in analog input applications is the impedance of the source signal. If the impedance is high, multiple problems can occur.
First of all, the voltage seen by the A/D will be reduced due to the voltage divider effect. From the equation, it can bee seen that the higher the source impedance R2, the smaller the voltage at the A/D and the larger the error. Conversely, the higher the input impedance of the board R1, the lower the resulting error. This is why the input impedance of the A/D board is a critical specification that should be examined during product selection.
Secondly, the source impedance will interact with stray capacitance in the input multiplexor chips on the A/D board, resulting in a low-pass filter that further reduces the input bandwidth of the board and causes cosstalk errors in multi-channel applications. If you are seeing crosstalk between input channels in your application, the first place to look is the source impedance of your inputs.